Understanding Pectoral (PEC) Nerve Blocks in Plastic Surgery
A Pectoralis block is a type of regional anesthesia used to relieve discomfort in the breast and chest region before, during, and after a variety of surgical operations, especially those involving the breast and chest wall. The target of the Pectoralis block is the pectoralis major muscle, a large muscle in the chest that affects the surrounding tissues and nerves. In order to effectively stop pain signals from reaching the brain, local anesthetic drugs are injected into particular muscle planes or gaps. Blocks minimize the need for opioid anesthesia and allow for patients to be more comfortable with fewer and less anesthetic medications.
Types of PEC Blocks:
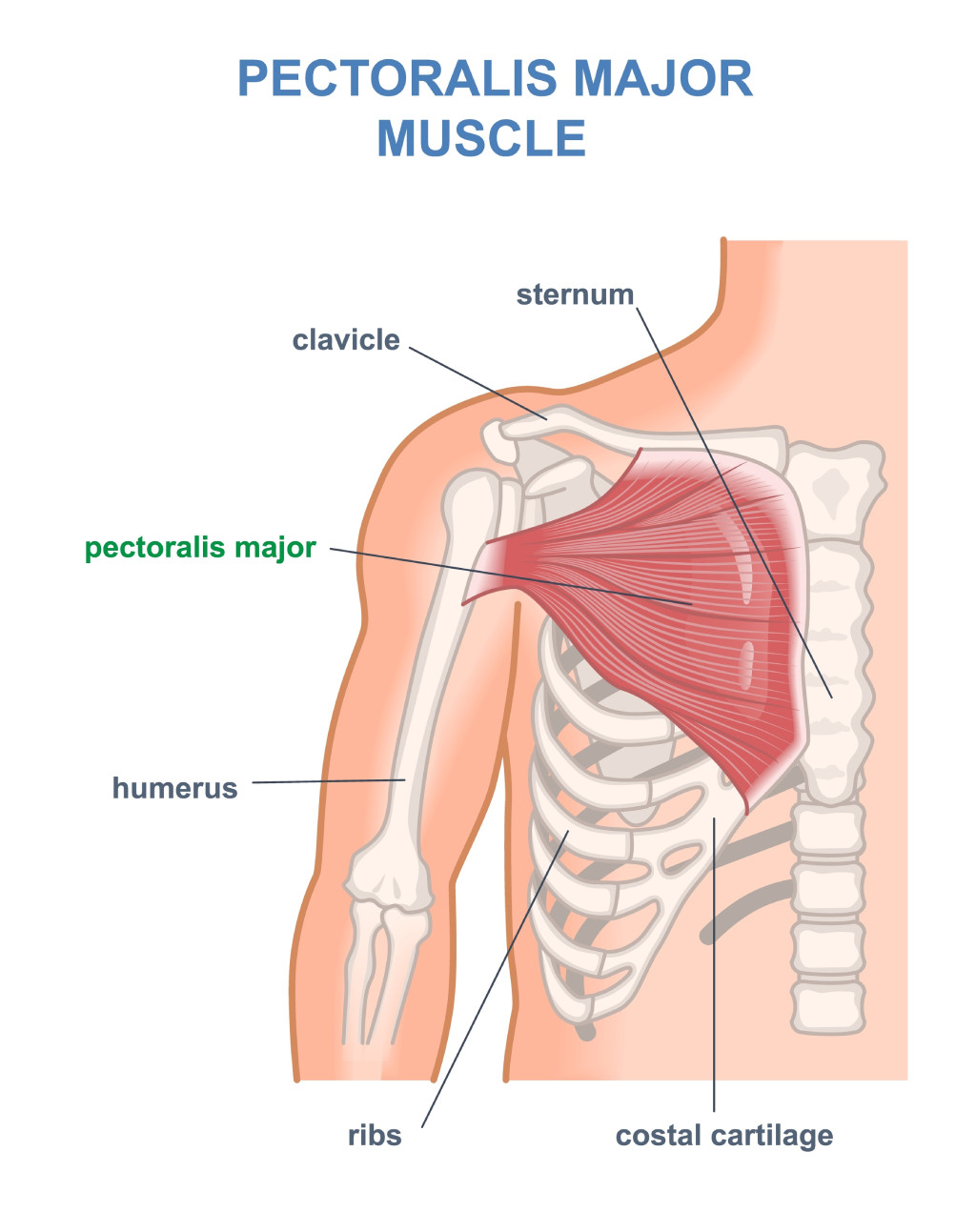
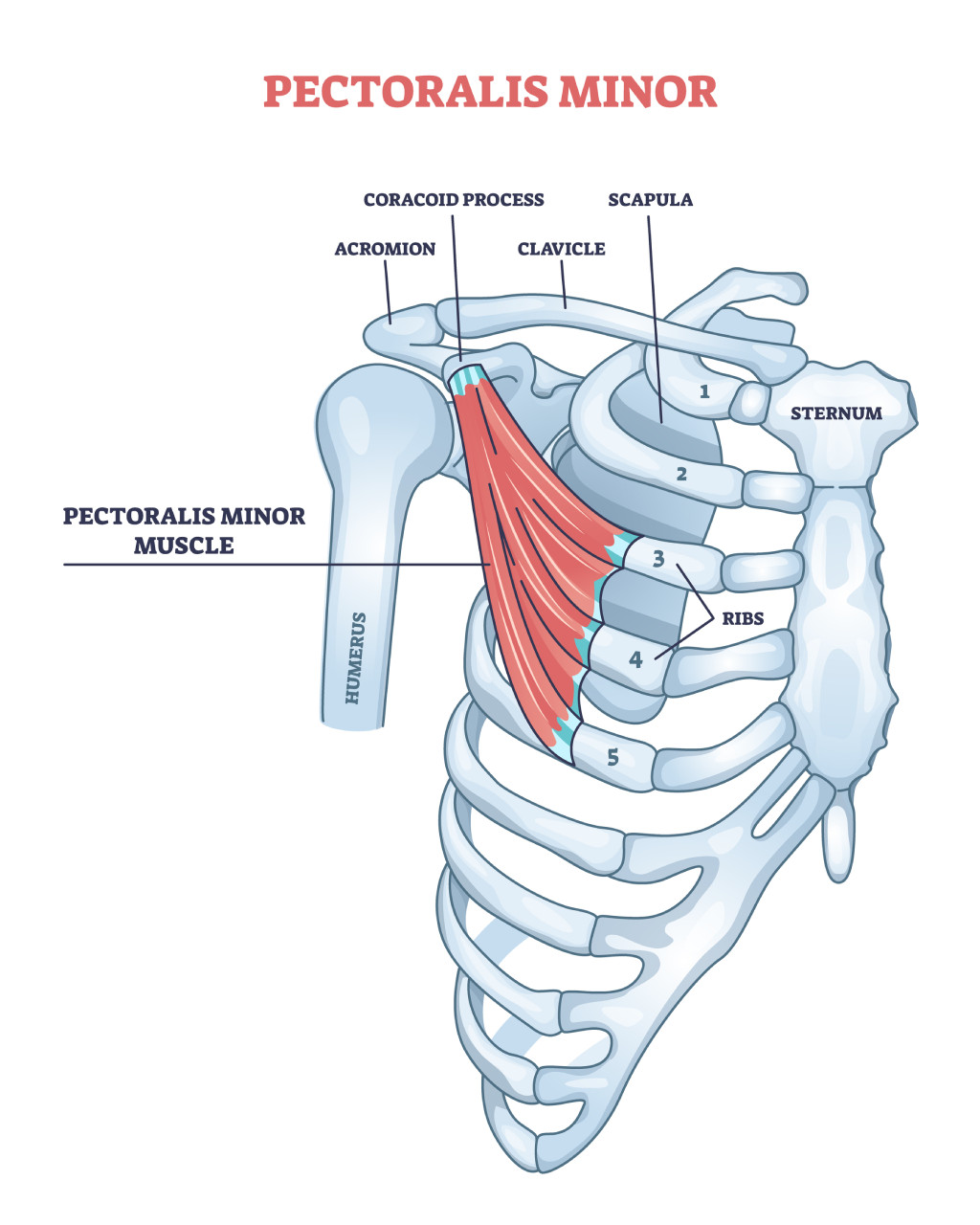
- Pectoralis Major Block (PECS I Block): This involves the injection of a local anesthetic between the pectoralis major muscle and the pectoralis minor muscle. It is often used for procedures involving the upper and lateral aspects of the breast, such as breast augmentation.
- Pectoralis Minor Block (PECS II Block): This involves the injection of a local anesthetic between the pectoralis minor muscle and the serratus anterior muscle. It is typically used for procedures involving the lateral and lower aspects of the breast, such as breast reduction or some gynecomastia surgeries.
These blocks are intended to minimize the need for opioid pain medications while effectively relieving pain during and after surgery. This can lead to improved patient comfort, faster postoperative recovery, and fewer opioid-related side effects. The decision to use PECS Blocks, whether PECS I or PECS II, is often based on the specific surgical approach and the patient’s needs. Board-certified plastic surgeon Dr. Azouz, in collaboration with the anesthesia team, tailors the anesthesia plan to align with the surgical objectives.
Administration of PEC Blocks in Surgery
PEC Blocks are typically injected before the start of surgery, during the preoperative phase. The specific timing of when the block is administered depends on the surgical and anesthesia team’s protocol and the patient’s needs. The duration of action for a PEC Block can vary depending on the type and concentration of the local anesthetic used, the patient’s metabolism, and the specific surgical procedure. In general, PEC Blocks can provide pain relief for a period of several hours, ranging from 4 to 12 hours.
- Preoperative Evaluation: Before the surgical procedure, the patient undergoes a preoperative evaluation, which may include discussions with the anesthesiologist and the surgical team. During this evaluation, the team will determine the most appropriate anesthesia and pain management plan, which may include the use of PEC Blocks.
- Anesthesia: Once the patient is in the operating room, the anesthesiologist typically administers sedation, and board-certified plastic surgeon Dr. Azouz typically administers the PEC Blocks. This is typically done after the patient has received necessary preoperative medications and monitors are in place.
- Block Administration: The PEC Block involves the injection of local anesthetic medications into the interfascial plane between the pectoralis major muscle and adjacent structures. The specific technique, whether it’s PECS I or PECS II, depends on the surgical procedure and the area that requires pain relief. The block is administered by Dallas plastic surgeon Dr. Azouz, the anesthesiologist, or a skilled healthcare professional with expertise in regional anesthesia.
- Surgical Procedure: Once the PEC Block has been administered and its effects have taken hold (typically a short time after injection), the surgical procedure begins. The block provides pain relief during the surgery, reducing the need for deeper forms of anesthesia and minimizing discomfort for the patient.
- Post-Operative Pain: After surgery, the sensory nerves in the chest and breast area transmit pain signals to the brain in response to tissue manipulation and surgical incisions. The anesthetic from the PEC Block prevents these nerves from transmitting pain signals, minimizing postoperative pain. Patients typically experience less pain during the recovery period, which can be particularly helpful during activities like coughing, deep breathing, or moving the arms.
Enhancing Patient Comfort and Pain Management in Plastic Surgery
Pec blocks are utilized in surgical procedures to improve patient comfort and pain management. Local anesthetics are injected between the ribs and the pectoralis major muscle, to target and numb sensory nerves around the chest area. Pecs Blocks greatly reduce the need for general anesthesia and often are critical in effective sedation anesthesia, which facilitates a more comfortable cosmetic or reconstructive procedure. This lessens the need for opioid painkillers, accelerating the healing process and enabling patients to get back to regular activities faster.
Examples of procedures using PEC Blocks:
- Breast Augmentation – PECS I Blocks are commonly used for breast augmentation.
- Breast Reduction – The choice between PECS I and PECS II Blocks for breast reduction may depend on the extent of tissue excision and the surgical approach.
- Gynecomastia Surgery – The choice between PECS I and PECS II Blocks may also depend on the surgical approach.
- Chest Wall Contouring – The choice between PECS I and PECS II Blocks in chest contouring can depend on the specific surgical approach and the areas that require pain relief.
The use of PEC Blocks is tailored to each patient’s specific needs and Dallas plastic surgeon Dr. Azouz’s recommendation. The decision to use these blocks depends on the patient’s medical history, preferences, and the complexity of the breast procedure.
Written by Anika Patel and Rhiya Patel on behalf of Azouz Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery
Posted on behalf of